相关服务
载体构建质粒DNA制备
病毒包装服务
mRNA基因递送解决方案
CRISPR基因编辑解决方案
shRNA基因敲低解决方案

在蛋白质合成过程中,密码子扮演着将基因信息翻译为蛋白序列信息的重要角色。
不同的物种翻译同样一个氨基酸可能使用不同的密码子,并且因物种不同而带有密码子偏好性。尽管目前尚未得知密码子偏好性的自然形成的原因,但是这种现象对于蛋白表达效率的影响是显著的。对于重组蛋白表达,为获得最佳表达效果,通常需要根据物种的密码子偏好性进行序列优化。特别是使用异源性的蛋白质表达系统时,由于来源于另一物种的目的基因需要在自然条件下不表达该基因的宿主中进行重组蛋白表达,这种优化因此显得更为重要。除此以外,密码子优化还具有其它应用,比如通过优化CG含量和重复序列区域以改善DNA克隆效率。密码子优化还应用在改善mRNA稳定性,增强转录和翻译效率等方面。
载体家密码子优化工具专为在特定物种中的目的基因表达而设计,并提供在特定物种中目的基因的最佳密码子适应指数(Codon Adaptation Index,CAI)。该工具包含一个全面的物种列表,同时无缝衔接我们的线上载体设计平台,有助您在设计载体时即可完成密码子优化。此外,该工具还提供不同的内切酶选项以规避优化后可能产生的酶切位点。我们的密码子优化工具还可以对高GC含量和简单重复序列等问题进行优化,最大程度满足基因合成和DNA克隆等应用需求。
以下各图展现了我们的密码子优化工具的多个功能。
图1展示了对粉纹夜蛾(Trichoplusia ni)的piggyBac转座酶的密码子人源化优化的结果。最终的优化序列的CAI值为0.93,优化前该值为0.63。某个物种对应的CAI值量化的是该物种中高表达的基因所偏向使用的密码子类型的频率。CAI值范围为0至1。目的基因的高CAI值意味着在该物种可以被更有效表达。

图1 使用载体密码子优化工具针对特定物种优化的基因序列
图2展示了小鼠Hoxa4基因的GC含量优化结果。使用我们的密码子优化过工具后,Hoxa4基因的GC含量从69.3%降至59.5%。对于基因克隆时需要合成的基因序列,最佳的GC含量应在60%左右,以增加基因合成成功的机率。
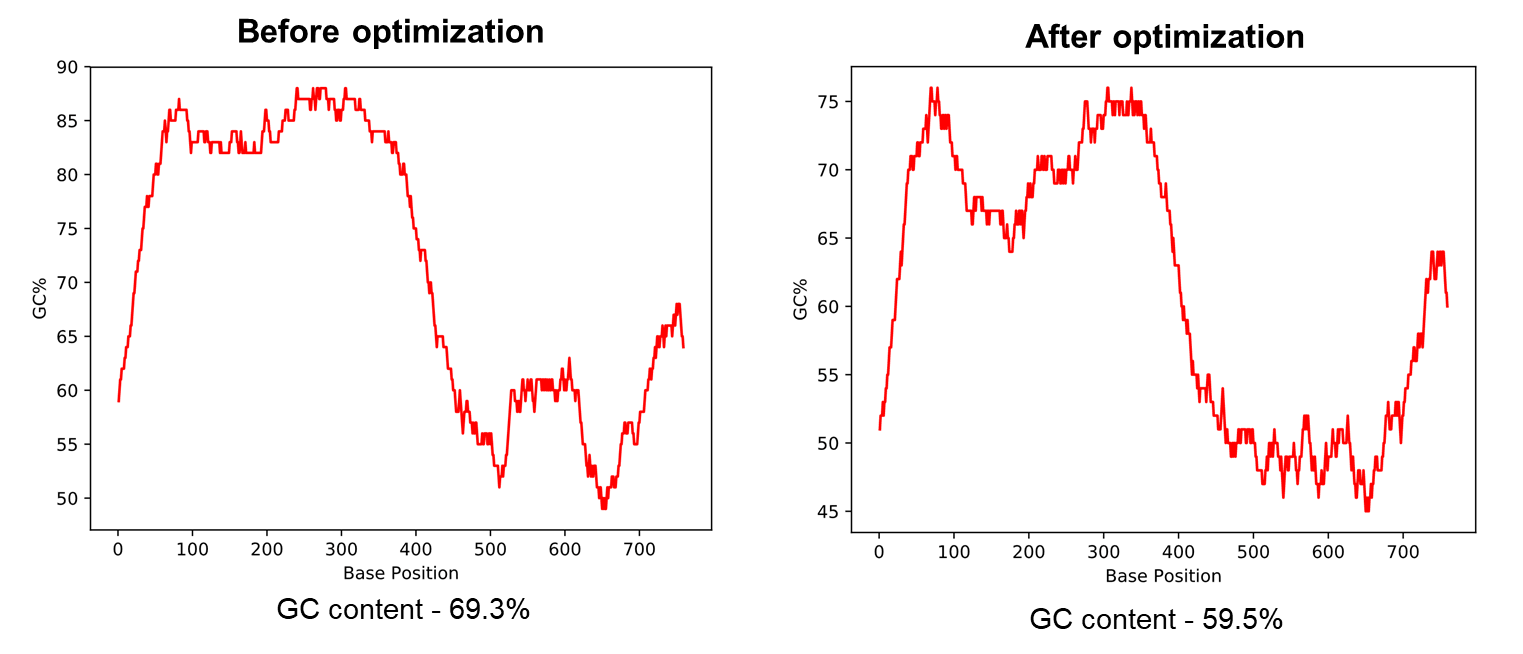
图2 使用载体家密码子优化工具降低高GC含量
图3展示了人免疫球蛋白序列自我比对的点阵图(Dot plot)。优化前点阵图中显著的对角斜线表明该基因包含大量的重复序列区域。优化后的点阵图中对角线图案消减,表明重复序列大为减少。
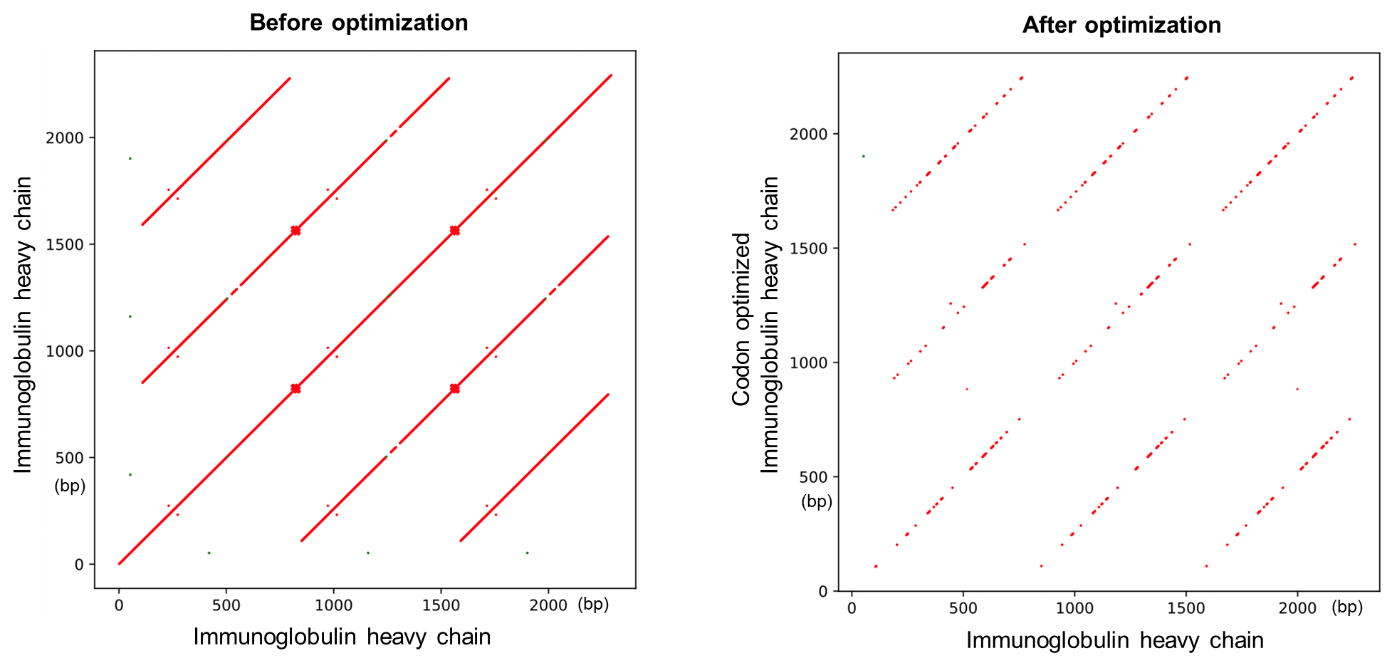
图3 使用载体家密码子优化工具减少重复序列区域
In order to produce proteins, a cell must first translate the relevant mRNA strand. Following transcription, the mRNA exits the nucleus where each group of three nucleotides is matched to a tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid (Figure 1A). These groups of 3 nucleotides are codons, and each corresponds to an amino acid. Because there are only 20 amino acids and many more possible combinations of nucleotides, there is redundancy in this code (Figure 1B).


Figure 1. Formation of a protein through transcription and translation (A) of codons. Each codon corresponds to an amino acid or direction (start/stop).
Although there are multiple options for making each amino acid, their usage is not based on chance. This is because each species exhibits codon bias, the preference for making an amino acid with a certain codon. For instance, alanine (Ala) is coded by GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG (Figure 1B), but in humans, GCC is used about 40% of the time. Different organisms have different codon preferences, which influences RNA processing and therefore protein folding and function. This creates complications when expressing one gene in another organism, i.e. heterologous gene expression.
The Codon Adaptation Index (CAI) is a measure of how well given codons match with the biases of an organism, ranging from 0 to 1. A CAI of 1 reflects a coding sequence where all amino acids reflect the most frequently used codons in that organism. Our Codon Optimization tool presents a sequence that balances an optimal CAI with other factors that can influence molecular experiments.
Codon optimization can also aid in increasing cloning efficiency based on the distribution of nucleotides across the sequence. GC content is an important variable to consider when designing and troubleshooting experiments. If GC content is too high or too low, stability of the query sequence is negatively affected. Our GC Content Calculator tool allows for independent GC analysis over an entire sequence and within segments of a sequence. However, our Codon Optimization tool incorporates this analysis to optimize this variable by finding synonymous codons that increase or decrease GC content as needed.
Additionally, sequences that have a high frequency of repeats can present complications in cloning efforts due to the lack of unique primer binding sites, and sequences with recognition sites for restriction enzymes can present challenges in experimental design. Using our Codon Optimization tool allows for all of these factors to be optimized in unison with codon bias to provide a sequence that is most likely to efficiently produce your protein in your system.